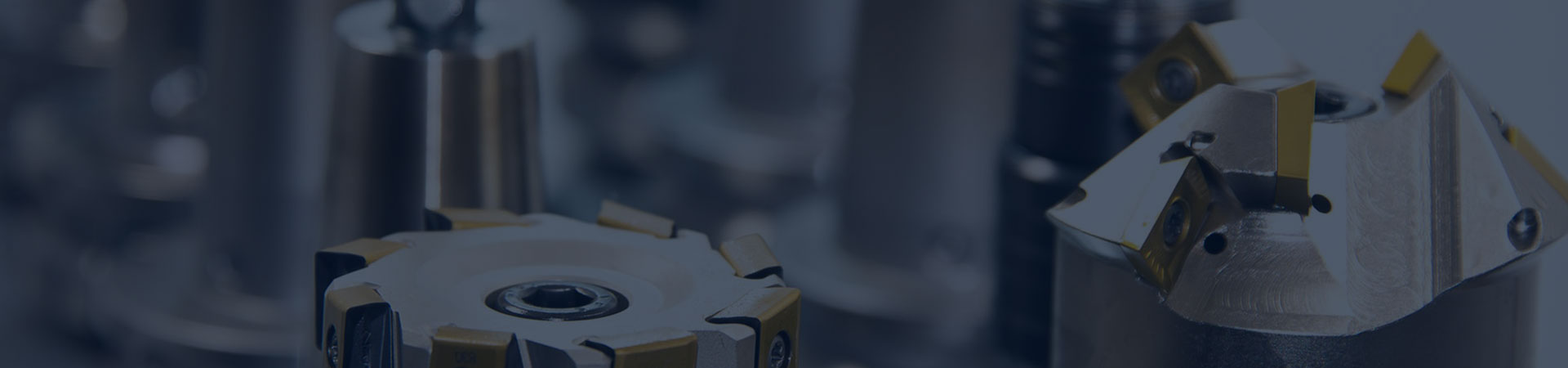
The structure and type of stern tube bearings
The stern tube bearing is used to support the stern shaft. The stern tube of a single axis system is usually equipped with two bearings, front and rear; Two bearings are installed in the stern shaft of a twin axis ship, and bearings are also installed in the herringbone frame. Stern tube bearings can be classified by material, mainly including white alloy bearings, iron pear wood bearings, rubber bearings, and so on.
Overview
The stern tube bearing is used to support the stern shaft. The stern tube of a single axis system is usually equipped with two bearings, front and rear; Two bearings are installed in the stern shaft of a twin axis ship, and bearings are also installed in the herringbone frame. There are many materials used for stern tube bearings, which can be divided into two categories: metallic materials and non-metallic materials. Metal materials mainly include bronze and white alloy. Non metallic materials mainly include iron pear wood, rubber, laminated wood, plywood, nylon, plastic, etc. Metal materials mainly include iron pear wood, rubber, laminated wood, plywood, nylon, plastic, etc. Stern tube bearings made of metal materials are generally cooled with oil lubrication, as sealing devices are installed at the front and stern ends of the stern tube, known as closed lubrication; Bearings made of non-metallic materials are generally lubricated and cooled with outboard water, and only a sealing device is installed at the head end of the stern tube. The outboard water can freely flow into the bearing, hence it is called open lubrication.
For more stern tube bearings information, kindly please click here.
For more marine shaft system components, kindly please click here.
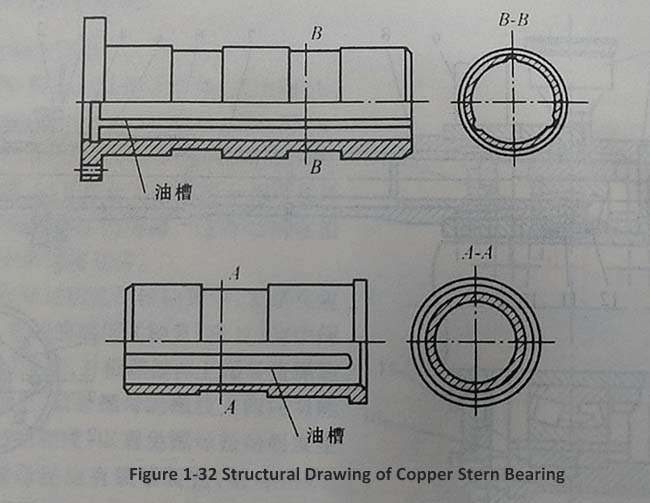
1. Bearing liner (Figure 1-32)
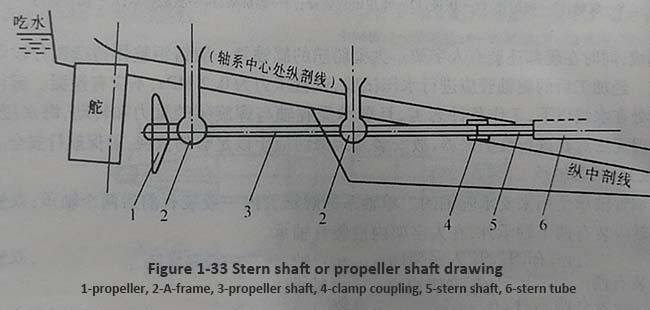
The basic structure of stern tube bearings is shown in Figure 1-33.
Small inland vessels below 100000 kilowatts generally use this structure. It is usually cast in bronze and then processed. Its characteristics are simple structure, easy manufacturing, but poor wear resistance.
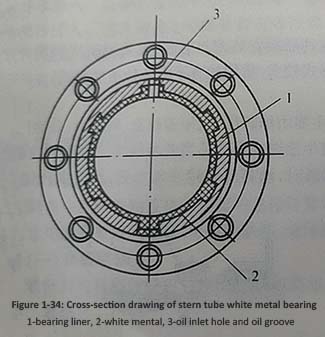
2. White mental bearings
White mental bearings are developed on the basis of copper bearings. The inner surface of the white alloy bearing liner is made of several longitudinal and transverse dovetail grooves and cast with white alloy. Its structure is shown in Figure 1-34, characterized by good wear resistance, high compressive strength, less wear, good heat dissipation, and no damage to the shaft neck. Its disadvantage is that the manufacturing and repair processes are complex and costly. This type of bearing is currently widely used on various types of ships.
3. Iron pear wood bearings
Iron pear wood is currently the most widely used material for stern bearings on ships. It is tightly organized, rich in resin, and has good corrosion resistance. Its semen and water can form an emulsion and have good lubrication effect. Iron pear wood and stern shaft bronze sleeve are rubbed together in water and have good wear resistance.
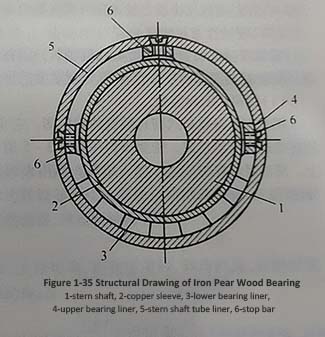
Figure 1-35 shows the structural diagram of iron pear wood bearings. Iron pear wood strips are tightly embedded along the axial direction of the liner on the inner circle of the stern tube liner, forming a barrel shape. To prevent the rotation of iron pear wood, 2-3 stop bars are generally installed. The material of the stop bar is basically the same as the lining material, with a length slightly smaller than the total length of the lining, and a thickness of 60% of the thickness of the iron pear wood. It is fixed on the lining with countersunk screws. Note that the volume of iron pear wood increases when soaked in water, so the installation clearance is larger than that of white alloy bearings. Generally, it is 3% of the journal diameter plus I mm (usually the clearance of white alloy is about one thousandth). Iron pear wood is mainly produced in tropical South America, and is also planted in Xishuangbanna, China, with high import prices. It is not dry resistant and should be soaked in water during processing and installation to prevent cracking. Its density is 1.2 times that of water. Birch plywood is also used as a substitute for iron pear wood.
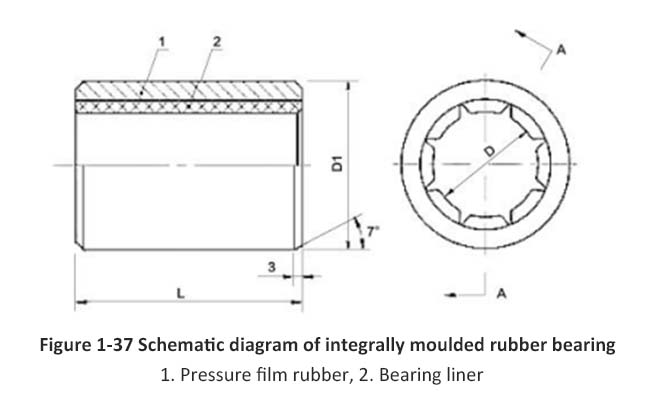
4. Rubber bearings
The characteristic of rubber stern shaft bearings is that they can work normally in waters with high levels of sediment and impurities. Because rubber has good elasticity, it can be applied in water areas with high sediment content. Rubber bearings have less wear than copper bearings or white alloy bearings, resulting in a long service life, smooth operation, no noise, and can absorb the vibration of the shaft system. The shaft can automatically adjust during operation. It is currently widely used in various ship stern shaft bearings, especially in small and medium-sized ships and engineering ships.
There are two basic structures for rubber stern bearings, one is rubber strip bearings and the other is integral molded rubber bearings.
Figure 1-36 shows the structure of rubber strip bearings. The rubber strip is similar to the iron pear wood strip, which is fixed in the metal bearing bush by small screws. In order to install and prevent loosening, 2-3 copper stop strips are often installed in a "barrel" arrangement in the middle of the rubber strip, with a length and width consistent with the rubber strip, but a thickness of 60% of the rubber strip. The stop strip is firmly connected to the bushing with countersunk screws, and a longitudinal water groove is opened between adjacent rubber strips to ensure that the bearing has sufficient water for lubrication and cooling.
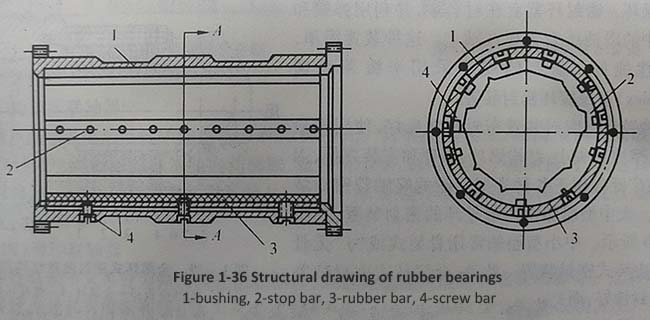
Figure 1-37 shows the integral molded rubber strip bearing. Its working surface has a raised shape. The concave groove is used for removing sediment and lubricating with water. This type of bearing is formed by groove pressing of chloroprene rubber or nitrile rubber at high temperatures. The structure of the overall transverse pressure rubber bearing is similar to that of the rubber strip bearing, but the process is different. Rubber strip bearings are suitable for small boats, while integral molded rubber bearings are suitable for both large and small boats, and are more reliable than rubber strip bearings.