Electrochlorination (EC) Ballast Water Management System
The electrochlorination ballast water treatment system is a technology used to handle the ballast water of ships.
Its working principle is to generate oxidants such as hypochlorite by electrolyzing seawater, and these oxidants can kill or remove invasive aquatic organisms in the ballast water, such as bacteria, plankton, eggs and larvae.
The electrochlorination ballast water treatment system has the advantages of high efficiency, rapidity, and a high degree of automation. It can handle a large amount of ballast water in a short time.
This article will introduce our electrochlorination ballast water management system to you, hoping to provide you with a solution!
Overview
Technical Characteristics
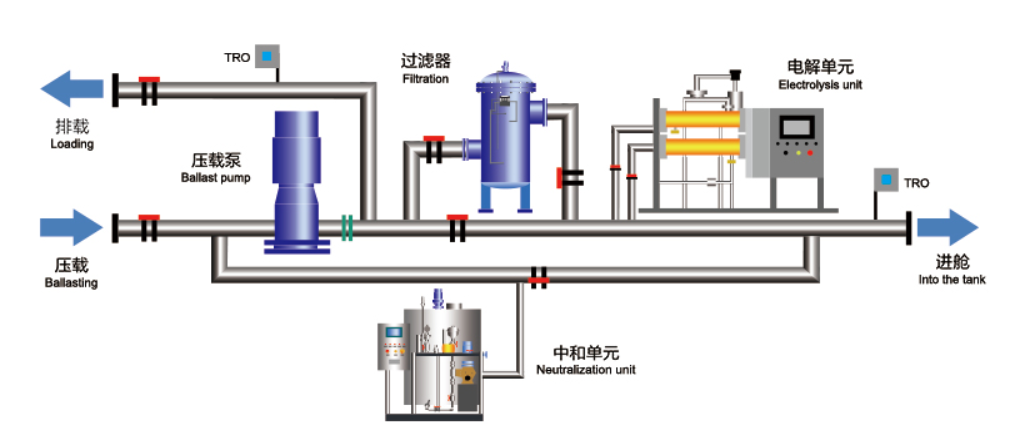
The treatment process of electrochlorination ballast water is divided into three steps: "filtration", "electrolysis of seawater to generate sodium hypochlorite for sterilization", and "neutralization":
Step 1: "Filtration" - When loading water, an automatic backwashing filter with a filtration accuracy of 50 um is used to filter all the ballast water. This step can filter out most of the marine organisms and solid particles larger than 50 um.
Step 2: "Electrolysis of seawater to generate sodium hypochlorite for sterilization" - Take a small flow of seawater from the main ballast water pipeline to flow through the electrolysis device, and electrolyze to generate a high-concentration sodium hypochlorite solution. After degassing, this solution is reinjected into the main ballast water pipeline and mixed and diluted with the ballast water in the main pipeline to a specific concentration. This concentration of sodium hypochlorite can effectively kill the remaining plankton, pathogens and their larvae or spores after filtration to achieve the specified sterilization effect (D-2 and other standards). The concentration of active substances in the ballast water pipeline is automatically controlled by the TRO analyzer and control system.
Step 3: "Neutralization" - When discharging the ballast water, when the residual chlorine concentration in the ballast water is less than the IMO-specified value, the neutralization system does not start and the ballast water is directly discharged to the destination sea area; when the residual chlorine concentration is greater than the IMO-specified value, the neutralization system automatically starts and injects a neutralizing agent into the drain pipe to neutralize the remaining oxidants. The flow of the neutralizing agent is automatically controlled by the control system according to the concentration information fed back by the TRO detector.
Description of the EC BWMS
Ballasting
During the ballasting process, the ballast water treatment system will be in a standby state until the flowmeter installed on the ballast main pipe detects the ballast water flow, and then the system will automatically switch to the running mode. Firstly, the ballast water passes through the filtering unit installed on the ballast main pipe to remove large plankton and solid particles. Subsequently, a side stream of the filtered ballast water flows through the electrolytic unit to generate sodium hypochlorite, which will be reinjected into the ballast main pipe and enter the ballast tanks for disinfection.
The by-product of electrolysis, hydrogen gas (H2), is separated and released through a cyclone separator to ensure that there is no H2 in the ballast pipe or ballast tanks. For safety considerations, two additional blowers are set in the electrolytic unit to dilute the hydrogen concentration to a safe level (<1%). Two sensors are also set to monitor the H2 concentration and air pressure so as to trigger the alarm once the H2 concentration reaches the preset value.
De-Ballasting
When de-ballasting, the neutralizer is added into the pipe in front of the ballast pump via the metering pump of the neutralization unit. With the agitation effect of the ballast pump, the neutralizer can react with the TRO quickly and completely. The concentration of TRO is monitored by the TRO analyzer at the ballast water discharge outlet. Once the TRO concentration exceeds the standard value, the control panel will give the alarm and display the state of the TRO concentration in excess and require the crew to stop the ballast pump.
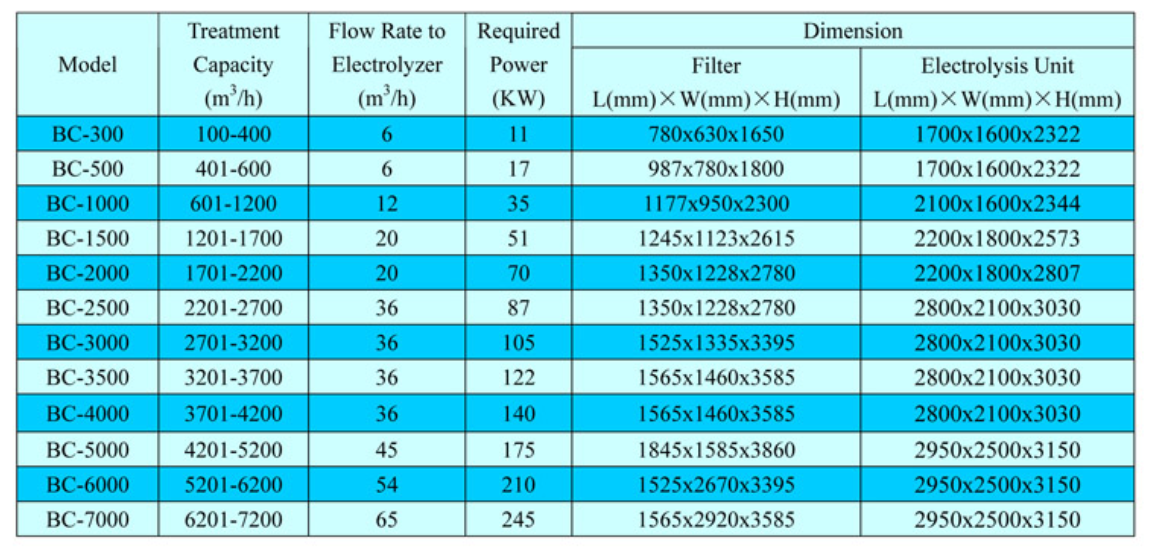
The Parameters of EC BWMS
The following parameters are available for your reference, and we can customize the design according to your needs.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have gained a certain understanding of our electrochlorination ballast water system through this article. We can also provide other types of ballast water management systems. You can visit our BWMS homepage to view or directly contact us.
If you have the need for procurement, please be sure to contact us, and we are always waiting for your arrival!

 Ballast Water Management System.jpg)



