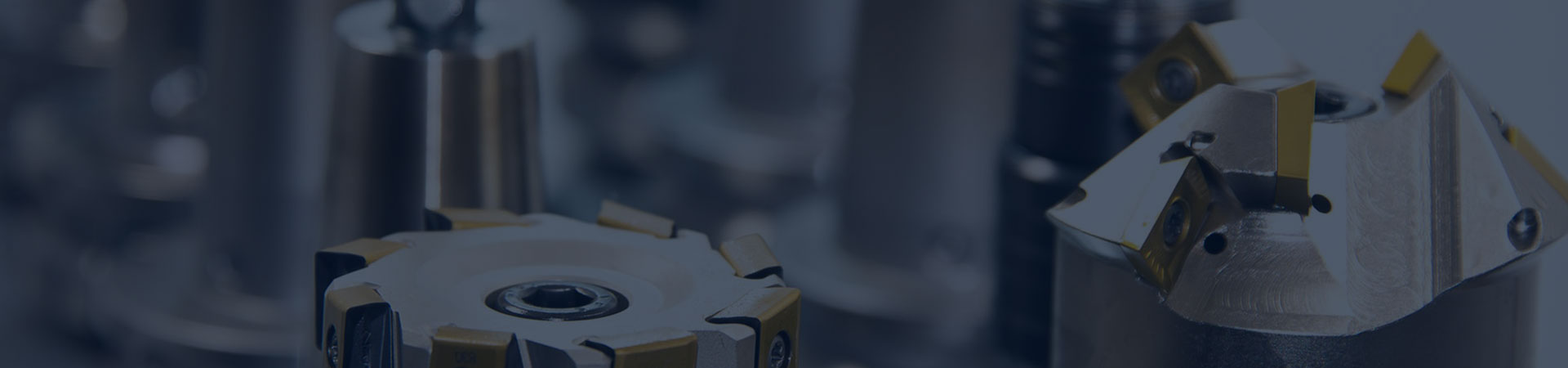
Chain hoist VS Lever hoist
Overview
External structure
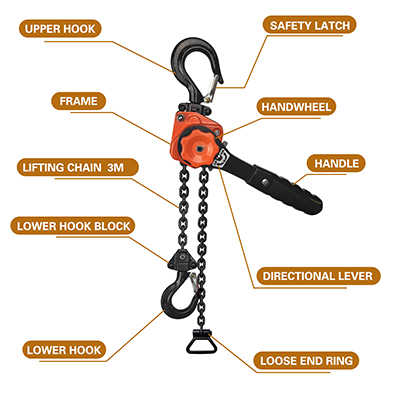
The hand chain hoist is typically supported by a main body frame, with a hand chain connected on top, and the operator applies force by pulling this hand chain. The lever hoist is commonly used in industrial applications and has a more complex structure. It has a handle, typically designed as a lever, connected to the main body structure through linkages and gear transmissions. The operator applies force by operating the lever on the handle. Briefly the structure of the hand chain hoist is relatively simple, while the lever hoist is more complex, containing more transmission components.
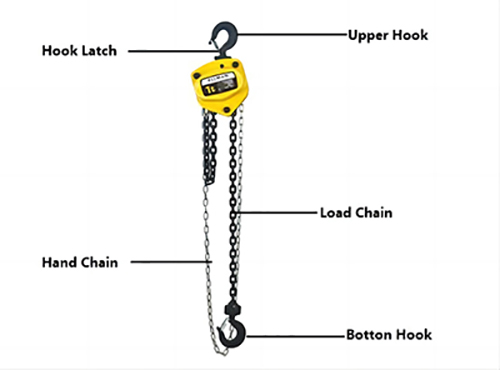

Working principle
Hand Chain Hoist: It operates by pulling the hand chain to drive internal components such as sprockets, friction plates, ratchets, and brakes, thereby driving the lifting chain to operate. The brake used in the hand chain hoist is a one-way brake, which can move freely within the load, and the pawl can drive the ratchet to rotate through the cooperation of the spring, ensuring that the brake can function properly.
Working principle of hand chain hoist
Hand lever hoist: By operating the hand lever handle and leveraging force through a lever, the lifting chain is activated for operation. The hand lever hoist has three additional positions compared to the hand chain hoist: upper gear, neutral, and lower gear. When the handle is in the upper or lower gear, the lifting chain can be raised or lowered. When the handle is in neutral, the position of the hook can be adjusted by manually pulling the lifting chain.
How A Lever Hoist Works
Applications
Hand chain hoists are commonly used in factories, docks, warehouses, construction sites, and other places for production, construction, and lifting of goods. In addition to standalone use, they can also be paired with different models of trolleys to turn into hand-operated lifting and transport trolleys for horizontal movement and lifting of goods.
Hand lever hoists are smaller in size compared to hand chain hoists and have a wider range of applications. They are commonly used in industries such as shipbuilding, electricity, transportation, and construction for equipment installation, lifting of goods, and mechanical traction.