Technical Points for Marine Pump Selection
Marinepumps,ascoreequipmentinaship'spowersystem,auxiliarysystem,andsafetysystem,theirrationalselectiondirectlyaffectstheship'soperationalefficiency,safety,andeconomy.Duringshipdesignandconstruction,theselectionofmarinepumpsrequirescomprehensi...
Overview
Marine pumps, as core equipment in a ship's power system, auxiliary system, and safety system, their rational selection directly affects the ship's operational efficiency, safety, and economy. During ship design and construction, the selection of marine pumps requires comprehensive consideration of multi-dimensional technical factors, not only to meet the functional requirements of various ship systems but also to comply with international industry regulations and standards.
I. Key Technical Indicators for Selection
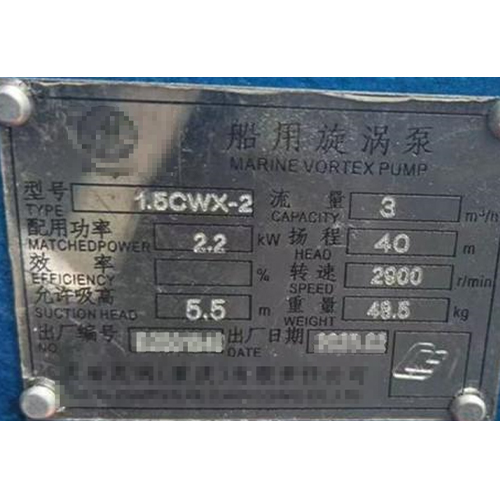
The selection of marine pumps focuses on seven core indicators: application scenarios, head, flow rate, self-priming performance, material compatibility, adaptability to installation environments, and classification society certification requirements. These indicators are interrelated, and optimal matching must be achieved through systematic analysis. The main specifications are shown in the following figure:
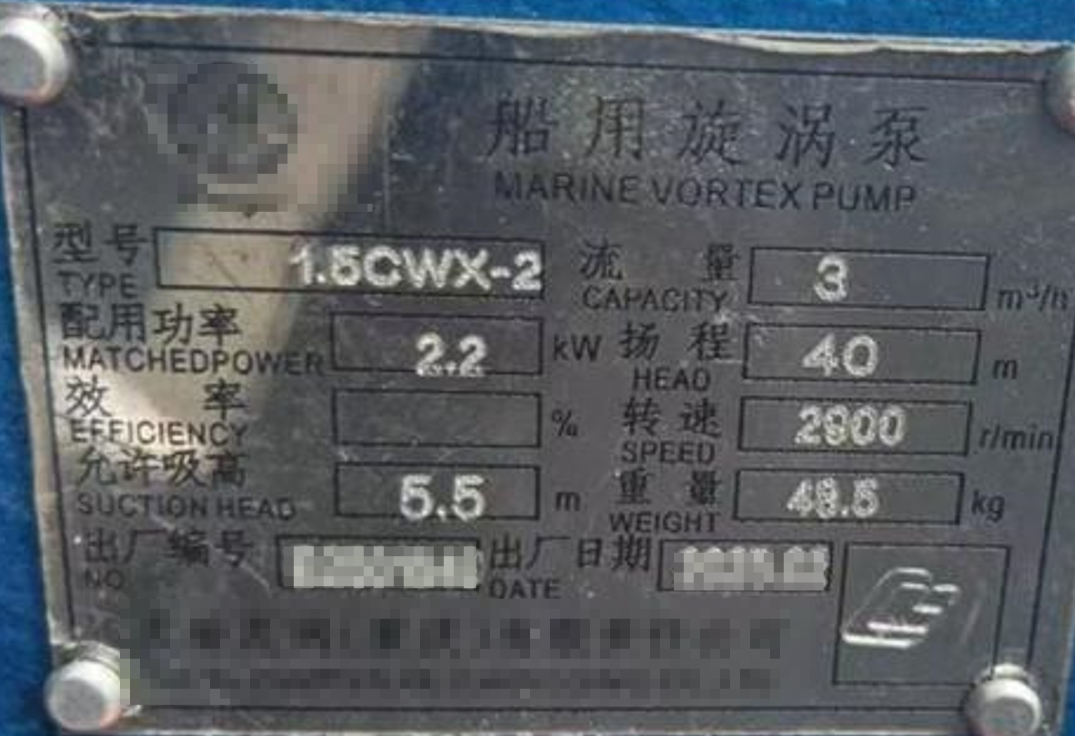
Vortex pump nameplate
II. Technical Adaptability to Application Scenarios
Different systems on ships have significantly different functional requirements for pumps, requiring precise selection based on system characteristics:
1.Ballast Water System
Technical requirements: Meet the needs of rapid loading and unloading of ballast water; large-flow centrifugal pumps are required.
Key parameters: Flow rate is usually ≥50 m³/h.
2.Fuel/Oil System
Medium characteristics: Heavy oil has high viscosity (>1000 cSt), requiring positive displacement pumps for stable delivery.
Recommended solution: Gear pumps or triple-screw pumps, equipped with high-precision filtering devices (precision ≤20μm).
3.Cooling Water System
Seawater cooling: Centrifugal pumps made of copper or 316L stainless steel, combined with electrolytic anti-fouling systems to prevent marine organism adhesion.
Freshwater cooling: Centrifugal pumps made of cast iron, which have significant cost advantages and meet corrosion resistance requirements.
4.Bilge Drainage System
Core requirement: Self-priming height ≥5 meters, adaptable to ship tilting conditions.
Recommended type: Self-priming centrifugal pumps.
5.Fire Protection System
Performance indicators: Head ≥100 meters, meeting the fire water pressure requirements of the entire ship.
Emergency configuration: Diesel-driven fire pumps with an independent power source to ensure continuous operation in case of power failure.
III. Accurate Calculation of Head and Flow Rate
1.Head Calculation Model
H = Hz + Hf + Hp
Hz: Geometric head (vertical lifting height, unit: m).
Hf: Pipeline resistance loss (frictional + local losses, usually estimated as 15%-20% of the geometric head).
Hp: Terminal pressure requirement (e.g., fire protection systems require ≥0.5 MPa).
Case: Ballast pump of a bulk carrier
Vertical height difference Hz: 12 m, pipeline friction loss Hf: 4 m, outlet pressure Hp: 3 m.
Calculated head: 12 + 4 + 3 = 19 m. After reserving a 20% margin, a pump with a head of 23-25 m is selected.
2.Flow Rate Matching Principle
Theoretical formula: Q = P×η/2.73H (Q: flow rate in m³/h; P: shaft power in kW; η: efficiency).
Practical selection: Must be combined with the pump characteristic curve to ensure the operating point is within the high-efficiency zone (80%-110% of the rated flow rate).
IV. Differences Between Different Materials
The selection of materials for the flow-through components of marine pumps must balance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and economy. Typical applications are as follows:
1.Cast Iron
| Material Type | Representative Grade | Performance Advantages |
| Gray cast iron | HT200 | Low cost, good castability |
| Ductile cast iron | QT400 | High strength, excellent wear resistance |
2.Copper
| Material Type | Representative Grade | Performance Advantages |
| Tin bronze | ZCuSn10Zn2 | Excellent corrosion resistance in seawater |
| Silicon brass | ZCuZn16Si4 | Strong resistance to electrochemical corrosion |
3.Stainless Stee
| Material Type | Performance Advantages |
| 316L | Resistant to acid and salt spray |
| Duplex stainless steel (2205) | - |
Stainless steel has stronger corrosion resistance than copper and other materials but has poor castability and high cost. It is generally used only for transporting strong acids, alkalis, and other media.
V. Installation Environment
1.Engine Room Space Optimization
Layout scheme: Vertical centrifugal pumps (saving 50% of floor space) or direct-coupled pumps.
Installation process: Elastic bases (rubber vibration isolators) + flexible pipeline joints to meet classification society vibration standards.
2.Hazardous Area Protection
Explosion-proof requirements: Cargo oil pumps must use explosion-proof motors (with Ex certification).
Considerations for frequency conversion: Frequency conversion motors must account for heat dissipation effects to avoid overheating.
VI. Classification Society Certification
1.Mainstream Classification Societies
CCS, RS, BV, DNV, LR, etc. Ships of different nationalities must select corresponding certifications.
Certification differences: Attention should be paid to the matching of certificate costs and technical requirements.
2.Key Certification Items
Type test: Hydrostatic test (1.5 times the rated pressure, no leakage for 30 minutes).
Material verification: Components in contact with seawater must provide material analysis reports.
VII. Conclusion
The selection of marine pumps is a complex systems engineering. It requires comprehensive consideration of installation environment, technical parameters, reliability, classification society certification, and other aspects, and adherence to scientific selection procedures to choose efficient, reliable, and safe marine pumps.