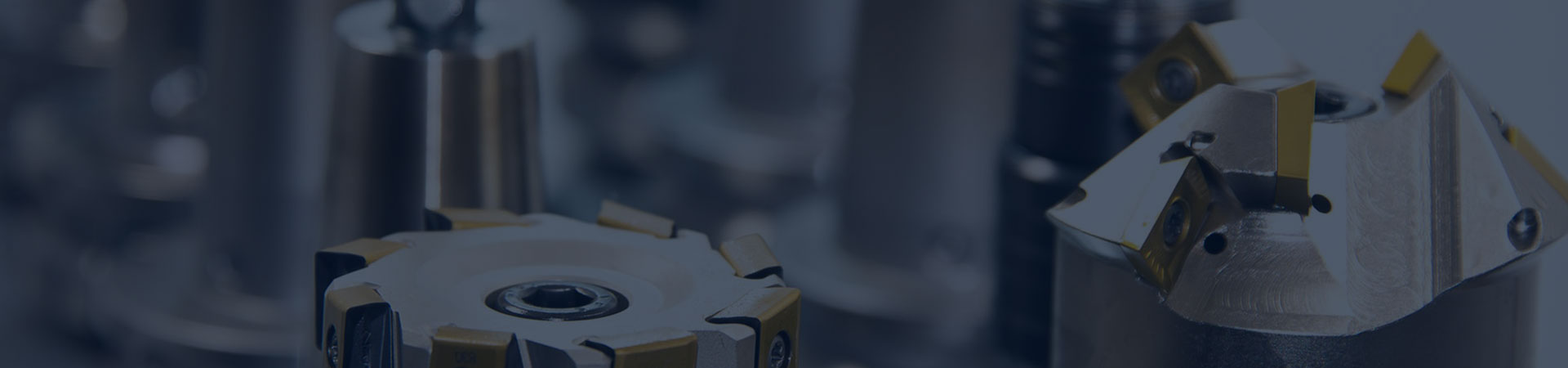
What is a thrust shaft?
The marine thrust shaft refers to the components used in the propulsion system of a ship to generate and transmit thrust. Typically, this system includes propellers (such as propellers) and mechanical devices that connect the propellers and power sources (such as engines). The main function of a marine thrust shaft is to transfer the power generated by the engine to the thrusters, thereby driving the ship forward. The thrust shaft is usually a shaft that is connected to the output shaft of the ship's power device and extends to the stern of the ship for connection to the thrusters.
Overview
Marine thrust shafts are usually designed to withstand high torque and tension, as ships are subject to various external forces during navigation, such as wind, surges, and water currents. Therefore, these thrust shafts are typically made of high-strength materials (such as alloy steel or stainless steel) to ensure their reliability and durability under harsh conditions. In summary, the marine thrust shaft is an important component of the ship's propulsion system, which plays a crucial role in transmitting power to the thrusters to propel the ship forward
Thrust shaft and its technical requirements
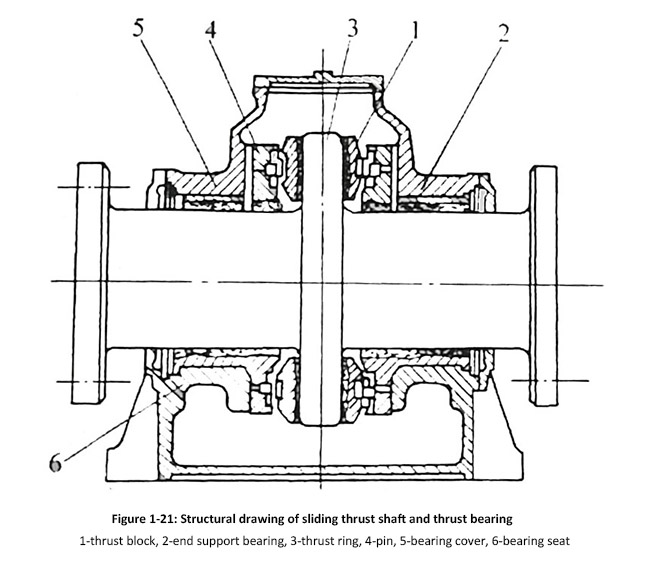
The thrust shaft can be divided into two types: multi-ring and single-ring. The multi-ring style, also known as the horseshoe style, has gradually been phased out. Single ring type, also known as Michel type, is currently a commonly used structural form for ships. Figure 1-21 shows the construction of a single-ring thrust shaft. The thrust ring and shaft are forged as a whole, with integral flanges at both ends, one end connected to the output shaft flange of the main engine, and the other end connected to the intermediate shaft.
For more marine thrust shaft information, kindly please click here.
For more marine shaft system components, kindly please click here.