What is a thrust bearing?
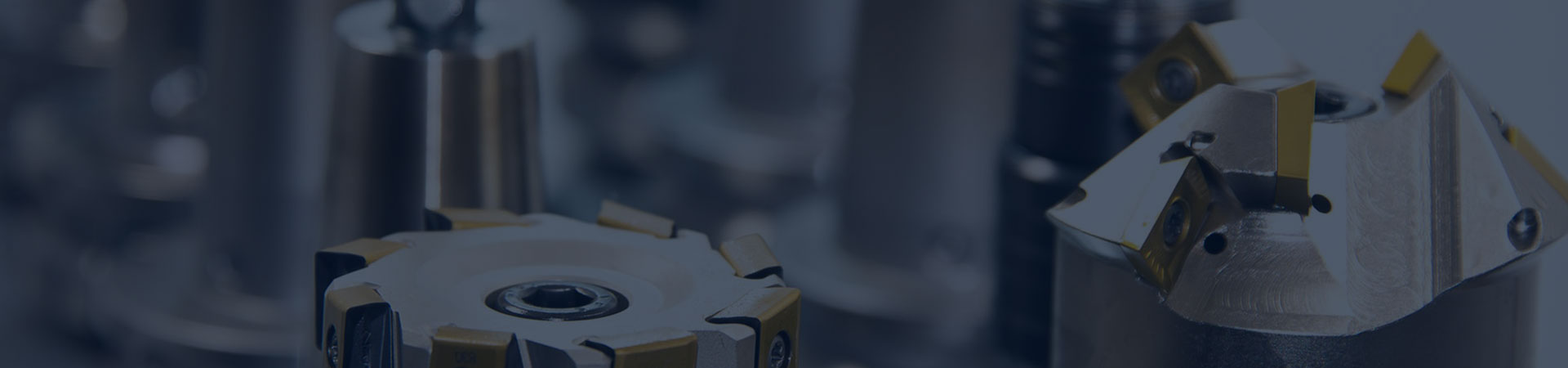
Marine thrust bearings are key components in ship propulsion systems, used to support and withstand thrust loads on the thrust shaft. These bearings are designed to cope with high torque and thrust, ensuring stable operation of the thrust shaft and effectively transmitting power to the thrusters.
Overview
The thrust shaft and thrust bearing are one of the important components in the ship's shaft system, with two functions: firstly, they bear the axial thrust generated by the propeller and transmit it to the ship's hull, making the ship move forward or backward; secondly, they maintain the correct axial position of the entire shaft system. If there is no thrust shaft and bearings, the thrust generated by the propeller will directly push the crankshaft of the main engine, causing it to bear great axial force, causing the crankshaft to move or tilt, thereby causing damage to the main engine components.
For more marine thrust bearing information, kindly please click here.
For more marine shaft system components, kindly please click here.
Thrust bearings and their technical requirements:
Thrust bearings are divided into two types: sliding and rolling, and currently the most commonly used is the submersible type.
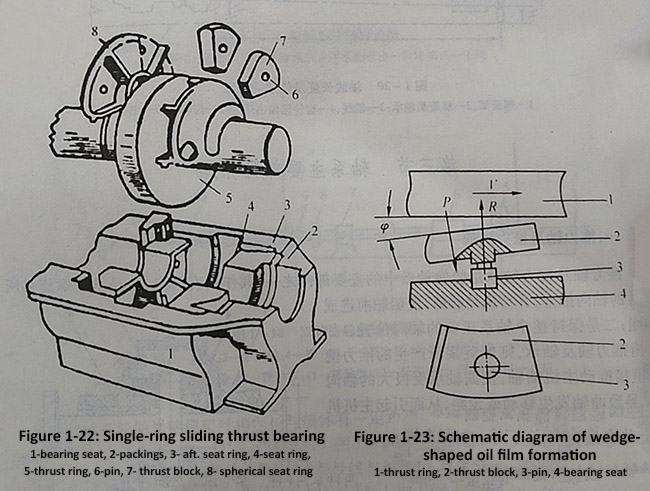
1. Figure 1-21 shows the structural diagram of a sliding thrust bearing. It consists of fan-shaped thrust blocks 1 supporting bearings 2, bearing west 5, and bearing seat 6 at both ends. The thrust shaft is supported on the supporting bearing, and the thrust blocks are distributed at the front and rear ends of the thrust ring 3, as shown in the figure- 22 is a schematic diagram of a single ring sliding thrust shaft commonly used on large and medium-sized ships.
The thrust block on the front end face bears the thrust of the main engine's main vehicle. The side where each thrust block is connected to the thrust ring is cast with bearing alloy. The back of the thrust block is supported by pin 4, which is eccentrically placed against the oil pressure center. When the thrust block is subjected to force, it can swing freely at the energy point of the pin, so it is also known as a moving block sliding thrust bearing. In this way, a wedge-shaped oil film can be formed between the thrust ring and thrust block during operation, thereby reducing frictional resistance.
The formation principle of wedge-shaped oil film is shown in Figure 1-23. When the thrust ring moves in the direction of the arrow and is pressed against the thrust block by the propeller thrust, the total force exerted by the oil film between the friction surfaces on the thrust block does not pass through the ball fulcrum. Therefore, the lubricating oil pressure P and the fulcrum reaction force R form a force couple, causing the thrust block to tilt and form a wedge-shaped oil film, which can reduce friction resistance, improve transmission efficiency, and extend service life. In this way, good lubrication can be achieved on the thrust ring and thrust block during operation, and it can withstand large working pressure.
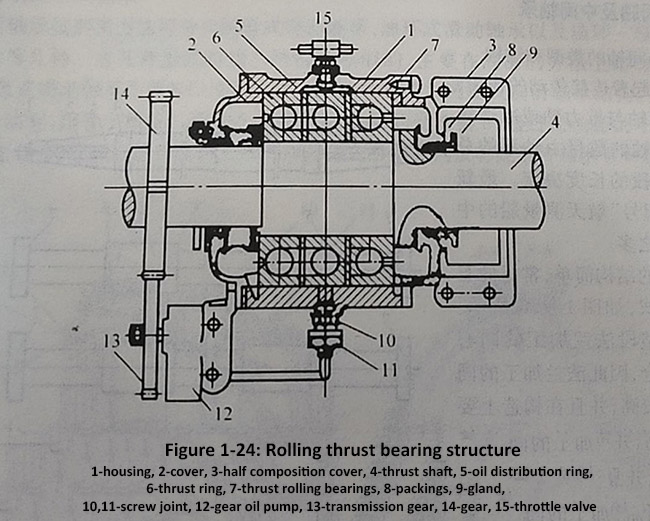
2. Figure 1-24 shows the construction diagram of a rolling thrust bearing. It consists of two thrust ball bearings with a sliding support bearing, bearing cover, bearing seat, etc.
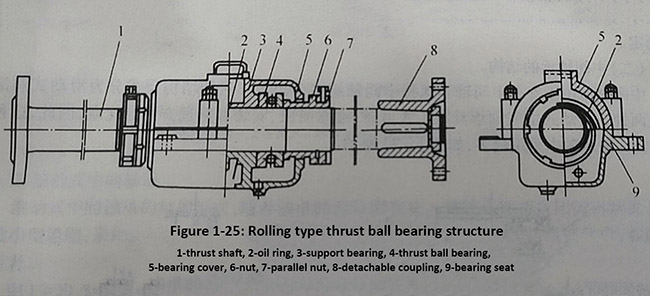
Due to the use of rolling thrust bearings, the thrust shaft does not need to be forged with thrust rings, and the connection method of one end (or both ends) of the thrust shaft must be made detachable, as shown in Figure 1-25.
Sliding thrust bearings, regardless of their structural form, require a certain axial clearance between the thrust ring and thrust block, which is necessary for the thermal expansion of the oil sliding film and parts. The adjustment of axial clearance is achieved by screwing in and out the supporting bolts installed on the bearing seat or adjusting the thickness of the cushion plate. In the installation of a direct drive shaft system, it is quite important that the axial clearance of the thrust bearing must be smaller than the axial clearance of the thrust bearing and connecting rod ends of the main engine itself, otherwise it will cause damage to relevant components of the main engine.
The maximum temperature of thrust bearings should generally not exceed 60C. And timely inspection and adjustment of the axis and the clearance between the bearings and the shaft should be carried out.





