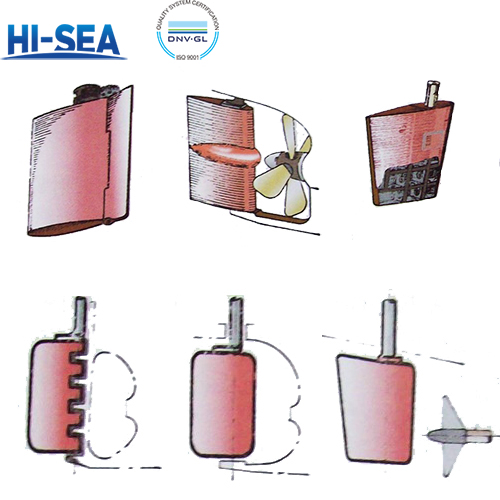
Types and structures of marine rudder
According to the cross-sectional shape of the rudder blade, there are flat-plate rudders (also known as single-plate rudders) and compound rudders ( streamlined rudders);
According to the type of support, there are double support rudders, multi-support rudders, suspended rudders, and semi-suspended rudders;
According to the axis position of the rudder stock, there are balanced rudder, semi-balanced rudder, and unbalanced rudder;
Overview
Type of rudder
According to different classification criteria, rudder has different classification methods. Its classification is as follows:
1. Classified by the axis position of the rudder stock:
(1) Unbalanced Rudder:
The axis of the rudder stock is located at the leading edge of the rudder blade, which means that the entire rudder area is distributed behind the rudder stock. Therefore, the water pressure center of the rudder is relatively far from the center of the rudder stock, and a larger turning torque is required when turning the rudder. At present, this type of rudder is rarely used in new shipbuilding. Its characteristics:
① The rudder blade area is all located behind the axis of the rudder stock.
② There are many steering buttons. (Multiple fulcrums, easy to ensure the strength of the rudder stock)
③ A larger turning torque is required when turning the rudder. (The center of water pressure is far from the axis of rotation)
(2) Balanced Rudder:
The area of rudder blades is distributed throughout the entire height before and after the axis of the rudder stock; A portion of its area is distributed behind the rudder stock, while another portion of the rudder area (known as the balance area accounting for 20% to 30% of the entire rudder area) is distributed along the rudder height in front of the rudder stock. Its characteristics:
① The area of the rudder blade is in front of the axis of the rudder stock.
② A smaller turning torque is required when turning the rudder. (The center of water pressure is close to the axis of rotation)
③ Application: Widely used on ships.
(3) Semi balanced rudder:
The lower half of the rudder is a balanced rudder, and the upper half is an unbalanced rudder. The balance ratio is below 0.2, suitable for ships with complex stern shapes.
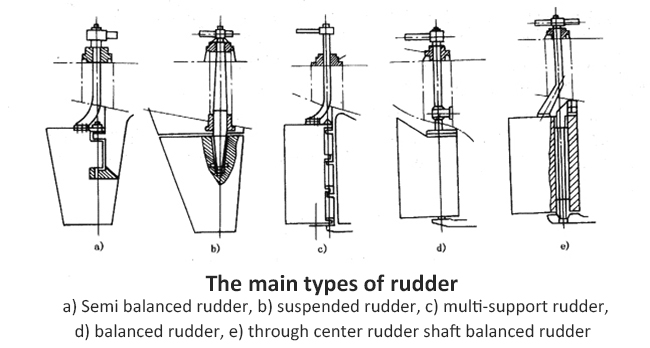
2. Classification based on the support of rudder blades:
(1) Multi pin rudder:
A rudder with two or more support points is called a multi support rudder.
① Supporting points: rudder bearing, rudder knob, rudder support.
② Connection between rudder knob and tail pillar: Use rudder pin connection.
(2) Double bearing rudder:
A rudder with two support points is called a double support rudder.
Support position:
① Upper support point: usually on the hull.
② Lower support point: Balance rudder: located at the rudder support at the lower end of the rudder blade. Semi suspended rudder: at half height of the rudder blade.
(3) Underhung Rudder:
A rudder with only support points inside the hull and all rudder blades suspended outside the hull.
(4) Partially underhung rudder:
There is only upper support without lower support, and the rudder blades are all suspended on the rudder stock outside the ship.
Features:
① The upper half of the rudder is supported by the rudder knob on the rudder post or rudder arm.
② The lower half of the rudder is supported at a height of half the rudder.
3. According to the cross-sectional shape of the rudder blade:
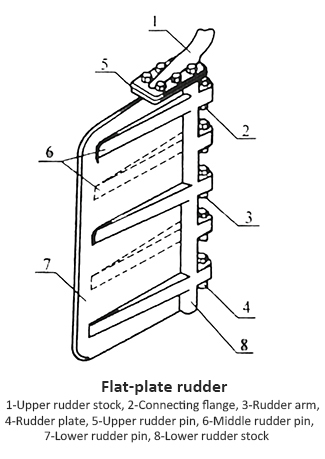
(1) Flat plate rudder, also known as single plate rudder
① Structure: The rudder blade is a steel plate or horizontally reinforced ribs (rudder arms) installed alternately on both sides of the steel plate.
② Feature: As the rudder angle increases, the efficiency of the rudder deteriorates. (Stall occurs early; resistance is also high)
③ Low strength and high resistance, used for non self-propelled ships, sailboats, or small boats.
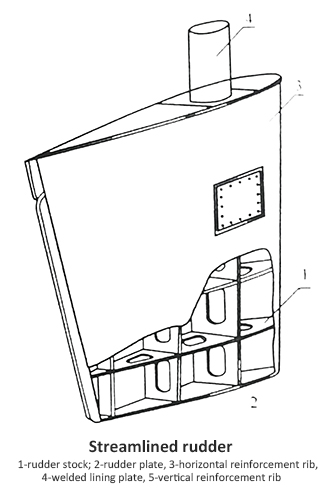
(2) Streamline rudder, also known as composite rudder
① Structure: The inside is a skeleton, the outside is a composite board, and the cross-section is streamlined.
② Features: High strength, the rudder blade profile is streamlined, partially hollow and watertight, generating a certain amount of buoyancy and reducing the force on the rudder bearing. Good hydrodynamic performance, large lift system of the rudder, low resistance, high steering efficiency. Although the structure is complex, it has many advantages and is widely used.
The structure of the rudder
The structure varies depending on the type of rudder. The structure of the streamlined balance rudder widely used on ships at present consists of rudder blades, rudder stock, and rudder bearings.
For more marine rudder system information, kindly please click here.