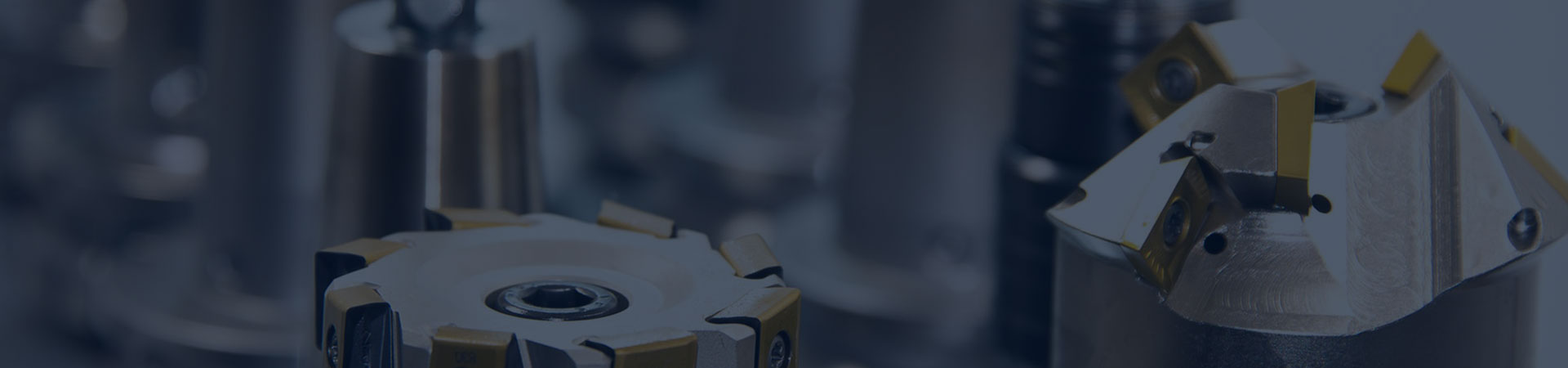
The structure and type of intermediate bearings
The intermediate bearing is used to support the intermediate shaft and maintain its axial position. These bearings play an important role in the power transmission system of ships, ensuring smooth rotation of the intermediate shaft and bearing various forces. It has two structural types: sliding intermediate bearing and rolling intermediate bearing.
Overview
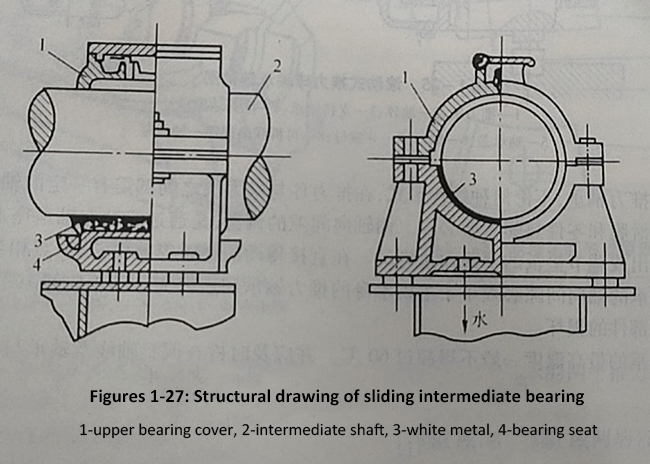
The intermediate bearing is used to support the intermediate shaft and maintain its axial position. It has two structural types: sliding and rolling. Sliding intermediate bearings have the advantages of reliable operation, simple maintenance, easy installation and repair. Therefore, this type of bearing is commonly used in general ships, as shown in Figures 1-27.
For more marine intermediate bearing information, kindly please click here.
For more marine shaft system components, kindly please click here.
1. Sliding intermediate bearing
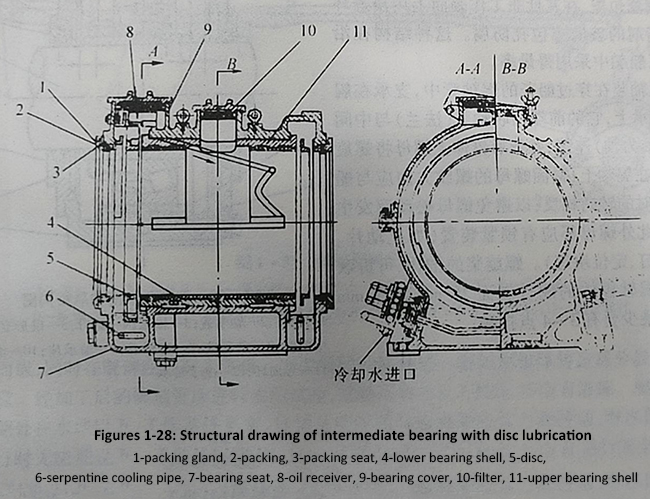
Intermediate bearings can be divided into several types according to lubrication methods, including disc type sliding bearings, oil ring type sliding bearings, and oil ring oil core composite sliding bearings. The basic structures of these types are similar, with slight differences in lubrication methods. Below, take the example of a circular sliding bearing for explanation. The structure of a disc lubricated bearing is shown in Figures 1-28. There are two oil chambers on the bearing seat, which are connected by pipes. The lower part of disk 5 is immersed in oil receiver 8, which flows through the small holes of the receiver to the diagonal direction, distributes to various lubrication parts, and finally flows back to the oil chamber at the bottom. The oil chamber is equipped with a serpentine cooling water pipe 6 for cooling.
2. Rolling type intermediate bearing
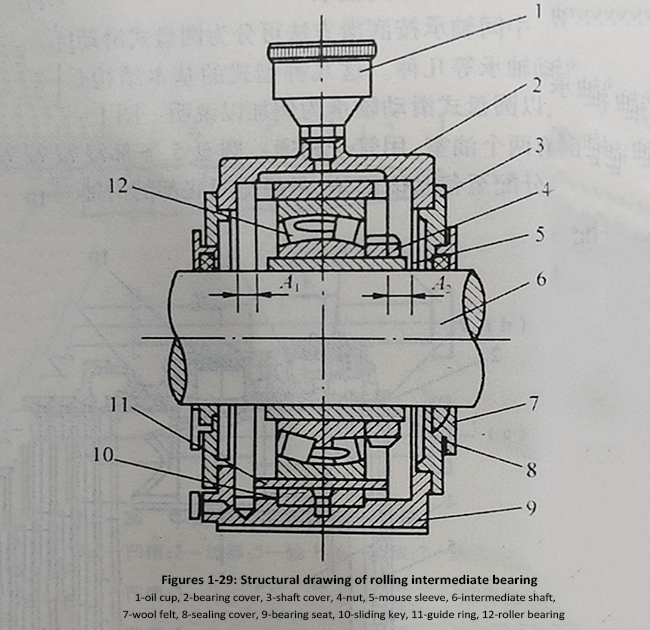
The structural form of rolling intermediate bearings varies with the type of bearing. Its bearing seat is usually made of cast steel. There are a few small ships that use steel plate welding structures. Its structure can be made into both integral and horizontal split types, with most using the latter.
Figure 1-29 shows a rolling intermediate bearing. The inner ring of the bearing is fixed to the intermediate shaft through a tapered sleeve 5 and a nut 4, and rotates together with the shaft. The outer ring is fastened to the bearing seat 9. When installing the roller bearing 12, the bearing should be installed on the journal first. In the free state, measure its radial clearance with a dial gauge, and then gradually tighten the nut of the conical sleeve. When the clearance is reduced to about 40%, it is considered to be firmly installed. When installing bearings with this structure, special attention should be paid to placing the roller bearings in the middle of the housing. The clearance dimensions A at both ends should be equal to A:, and it is strictly prohibited for A and A2 to be equal to zero. The height of the lubricating oil shall not be lower than the center position of the bearing:
Compared with sliding bearings, rolling intermediate bearings have the advantages of low friction resistance, high efficiency, low oil consumption, reliable operation, and automatic integration (i.e. the center line of the bearing can change with the axis). The main disadvantage is high working noise, and detachable couplings must be used.