Structure and Principle Analysis of Plate Heat Exchanger
Plate heat exchanger is a kind of highly efficient, compact and widely used heat exchange equipment. It is composed of a series of metal plates with specific corrugated shapes stacked and combined. The design of these plates enables the fluid to fully flow and exchange heat in a narrow space, greatly improving the heat exchange efficiency. The plate heat exchanger has many advantages, such as excellent heat exchange performance, which can quickly realize the transfer of heat; the structure is compact, occupying a small space and facilitating installation and layout; it has strong flexibility and can be flexibly combined and adjusted according to different needs.
Overview
The basic principle of the plate heat exchanger:
Plate heat exchanger is a common heat exchange equipment, used to transfer heat from one fluid to another without direct contact between them. The basic principle is to utilize the heat conduction between the metal plates to achieve the transfer of heat.
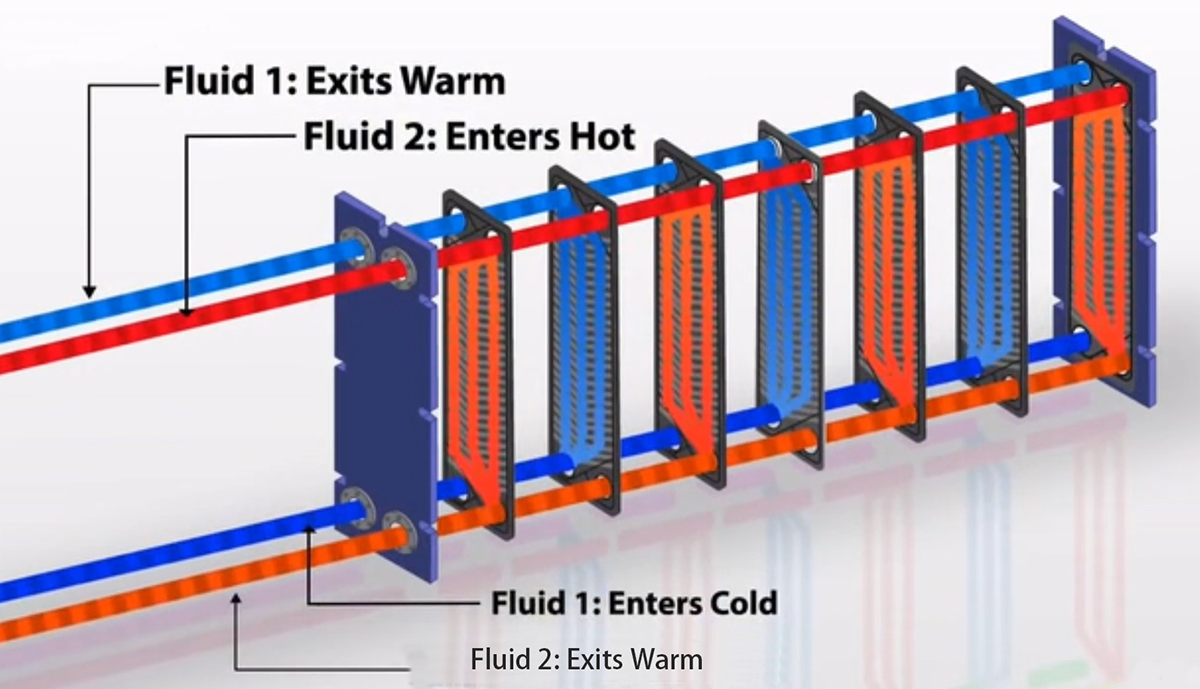
Structure: A plate heat exchanger is composed of a series of metal plates arranged in parallel, with a certain gap between the plates to form fluid channels. The fluids flow through these channels to conduct heat exchange.
Heat conduction: When two fluids with different temperatures pass through the plate heat exchanger, the heat will be conducted through the metal plates. The heat will be transferred from the high-temperature fluid to the metal plates and then to the low-temperature fluid. This process is achieved through heat conduction, and the thermal conductivity performance of the metal plates determines the efficiency of heat transfer.
Fluid flow: The fluids form a complex network of channels inside the plate heat exchanger and flow through these channels. Generally speaking, the fluids flowing in the designed channel network between the plates can better form turbulence and avoid laminar flow. And the turbulent fluid flow mode makes the heat transfer between the two fluids more effective.
Increased surface area: Due to the gap between the metal plates, the effective surface area of the plate heat exchanger is relatively large. This makes the heat transfer capacity per unit volume higher and the heat exchange efficiency better.
Types of plate heat exchangers:
Plate heat exchangers can be divided into the following types:
Detachable plate heat exchanger:
The plates are connected by detachable gaskets, which is convenient for maintenance and cleaning.
The number of plates can be flexibly adjusted to adapt to different working conditions.
The existence of gaskets may lead to a certain risk of leakage. But a leakage signal port can be designed through the gasket to detect the leakage in advance and avoid mutual seepage of media.Welded plate heat exchanger:
All the plates are connected by welding, with extremely good sealing performance and capable of withstanding very high pressure, and is very suitable for heat exchange of corrosive media.
It is almost impossible to disassemble, and the maintenance is rather difficult.
It is applicable to situations where the requirements for sealing and pressure resistance are extremely high and the medium is stable.Brazed plate heat exchanger:
The plates are connected by brazing process, and it has relatively good sealing performance.
It is relatively more compact in structure than the welded plate heat exchanger.
Similarly, it is difficult to disassemble, and the maintenance is greatly limited.Semi-welded plate heat exchanger:
Some plates are welded and some plates are detachable, possessing the characteristics of both welding and detachability.
It has better sealing performance and certain maintainability at the same time.
It can deal with more complex working conditions, providing certain flexibility while ensuring certain sealing and pressure resistance.
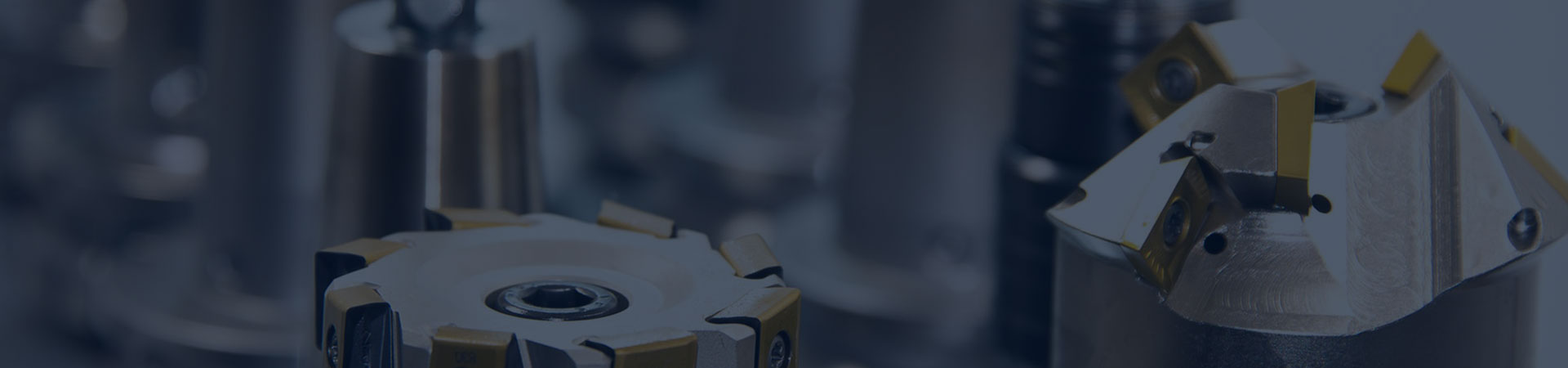
The main structure of the plate heat exchanger:
When it comes to the structure of the plate heat exchanger, it usually involves the following several main components:
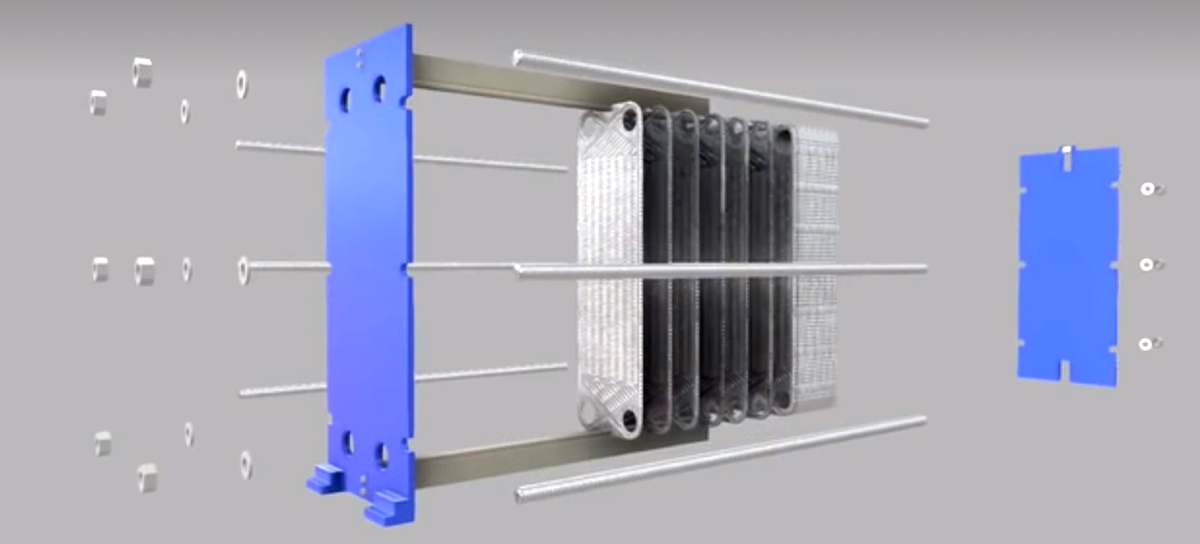
Heat Transfer Plates: One of the core components of the plate heat exchanger. These plates are usually made of metals such as stainless steel or titanium alloy. They are designed to have many small holes or wavy shapes to increase the surface area, thereby enhancing the heat transfer efficiency. The shape and arrangement of the plates have important impacts on the performance of the heat exchanger.
Gaskets: Elastic gaskets used to form sealed channels between the plates. These gaskets are usually made of rubber or synthetic rubber to ensure that the fluid does not leak when flowing between the plates. The gaskets can also help reduce the heat loss between the plates. It should be noted that in the structure of the welded plate heat exchanger, this structure is replaced by welding.
End Plates: Structural components located at both ends of the plate heat exchanger, used to support and fix the plate assembly and guide the fluid into the correct channels. The end plates are usually made of metal and have inlet and outlet pipes so that the fluid can enter and exit the heat exchanger.
Tightening Bolts: Bolts used to fasten the plates and gaskets together. These bolts pass through the holes in the end plates and are pressurized by fastening nuts or other fastening devices to ensure the pressure and sealing performance inside the heat exchanger.
Support Columns: Structural components used to support and fix the plate heat exchanger. The support columns are located at both ends of the plate heat exchanger and are connected to the end plates by bolts or other connecting elements to provide additional support and stability.
Shell: The external structure covering the entire plate heat exchanger, usually made of metal, used to protect the internal components from the influence of the external environment and provide additional support and protection.
These components together constitute the structure of the plate heat exchanger to ensure its normal operation and achieve efficient heat transfer. Different models and application fields of the plate heat exchanger may vary in structure, but the basic principles and components usually remain similar.
Conclusion:
The above is the entire content of this article. In the article, we have detailedly introduced to you the basic structure, types and basic principles of the plate heat exchanger. We hope that through this article, it can help you choose the plate heat exchanger.
Finally, if you have the need for procurement, you are welcome to visit our marine heat exchanger homepage or contact us at any time! Thank you again for your browsing!





