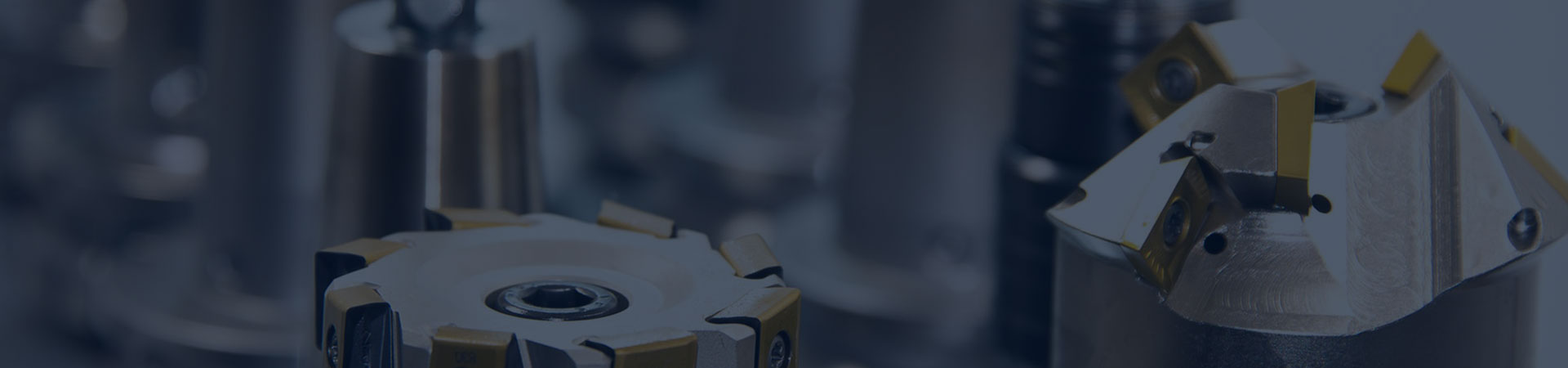
No heat regenerative adsorption dryer
No heat regenerative adsorption dryer is a device that uses an adsorbent to adsorb moisture from the air and perform non heat regeneration to achieve gas drying.
It is widely used in industrial gas processing, compressed air systems, and other fields, and can provide continuous, stable, and dry gas supply.
Main features: No heat regeneration, continuous operation, efficient adsorbent, energy-saving and environmental protection
Overview
Working principle
No heat regenerative adsorption dryers typically have two or more adsorption towers that alternate between adsorption and regeneration processes by controlling valve switching. The main process includes:
Adsorption stage:
Compressed air passes through an adsorption tower, where adsorbents (such as activated alumina and molecular sieves) adsorb moisture from the air, drying the output air.
Regeneration stage:
The other adsorption tower undergoes regeneration at this time. The regeneration gas without heat regeneration comes from the already dried air, which is throttled and depressurized before passing through the regeneration tower to remove the moisture in the adsorbent and discharge it out of the system.
Switching phase:
Adsorption and regeneration alternate, ensuring continuous and stable dry air output by controlling valve switching.
Main characteristics
No heat regenerative adsorption dryer is a process that uses dual tower pressure swing adsorption and no heat regeneration. Its working principle is that one adsorption tower performs adsorption drying under working pressure, while the other adsorption tower uses a portion of its own dry gas and depressurizes it to close to atmospheric pressure, using it as a regeneration gas for regeneration. The dual tower switches at a fixed switching time to continuously provide dry gas.
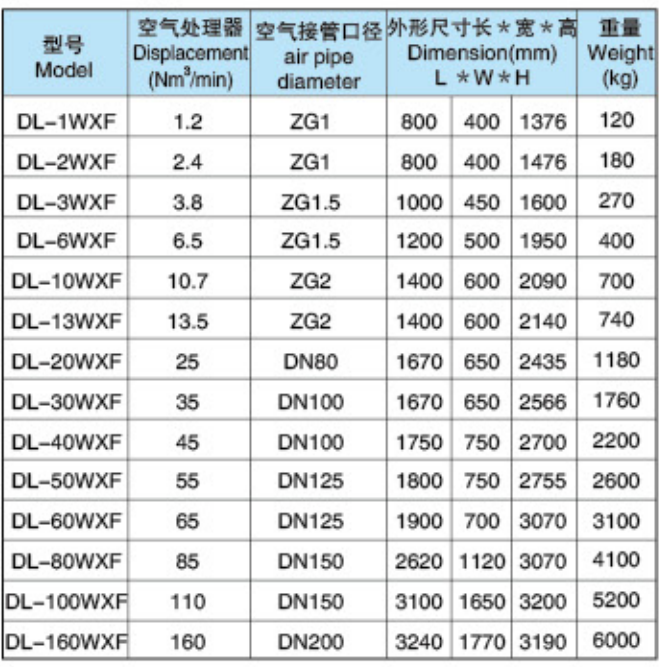
Main parameters: