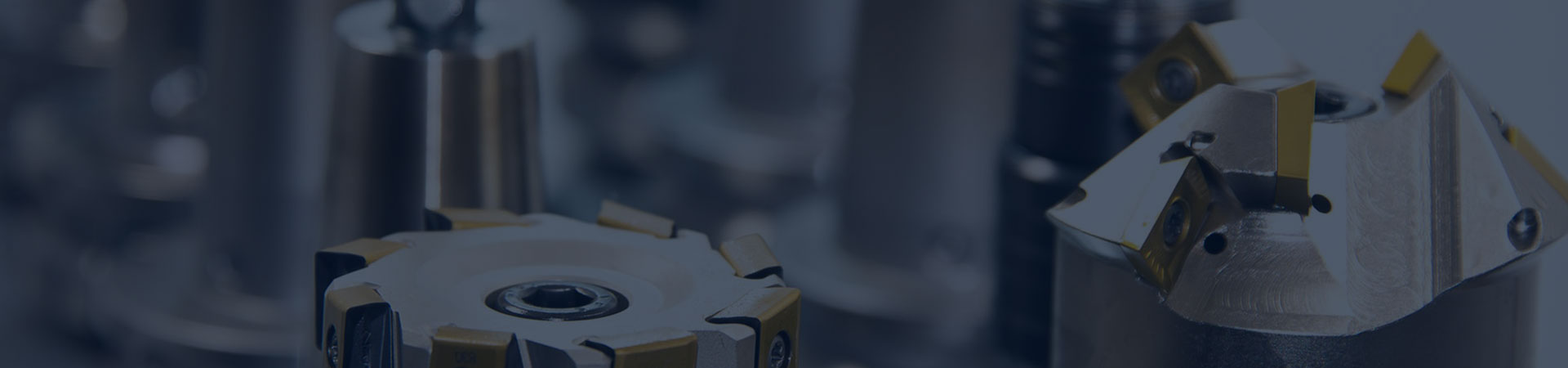
Marine Plate Heat Exchanger
Plate heat exchanger is composed of a group of corrugated metal plates with four corner holes for two kinds of liquids to flow through. The metal plates are installed in a frame, with a fixed pressing plate and a movable pressing plate on the side, and are clamped by clamping bolts. Sealing gaskets are installed on the plates to seal the fluid channels and guide the fluids to alternately flow into their respective flow channels to form heat exchange.
It has the characteristics of high heat exchange efficiency, low heat loss, compact and lightweight structure, small floor area, wide application and long service life. Under the same pressure loss, its heat transfer coefficient is 3 to 5 times that of tubular heat exchanger, and the floor area is one-third of that of tubular heat exchanger. The heat recovery rate can be as high as more than 90%. There are mainly two types of plate heat exchangers: frame type (detachable) and brazed type.
Overview
Plate Heat Exchanger Features
Plate heat exchangers are made of polymer synthetic fibers through special processes and have characteristics such as high moisture permeability, good air tightness, tear resistance, and aging resistance.
The energy-saving effect of plate heat exchanger products has reached the advanced foreign level. They have a long service life and good thermal conductivity and are suitable for areas with a large indoor and outdoor temperature difference and a small humidity difference.
Plate heat exchangers can be equipped with different functional sections such as heating, cooling, humidification, purification, and noise reduction according to user needs.
Plate heat exchangers are usually formed by high-temperature brazing in a vacuum with stainless steel (304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel), titanium alloy to form a brazed type, or locked into a combined type with sealing rings and bolts.
Plate heat exchangers form a compact plate heat exchanger that can withstand operation under continuous high temperature and high pressure conditions.
Basic Structure of Plate Heat Exchanger
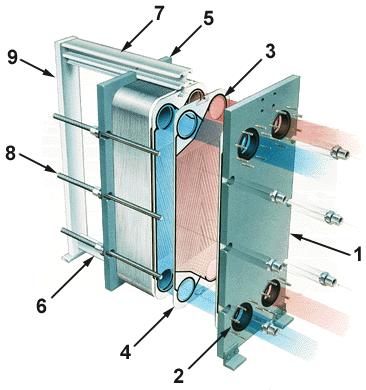
1. Fixed pressure plate; 2. Port; 3. Gasket; 4. Plate; 5. Movable pressure plate; 6. Lower guide rod; 7. Upper guide rod; 8. Compression screw; 9. Front support rod
Points to note when choosing a plate heat exchanger
The plate type or corrugated type should be determined according to the actual needs of the heat exchange occasion. If the flow rate is large and the pressure drop is small, the plate type with low resistance should be selected, otherwise, the plate type with large resistance should be used.
According to the fluid pressure and temperature, determine whether to choose a detachable or a brazed type. When determining the plate type, it is not advisable to choose a plate with a single plate area that is too small, lest there are too many plates, the flow velocity between the plates is too small, and the heat transfer coefficient is too low. This problem should be paid more attention to for larger heat exchangers.





