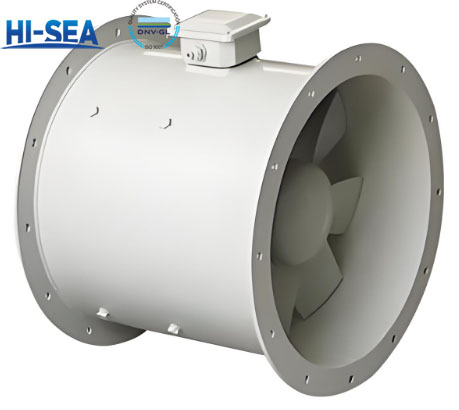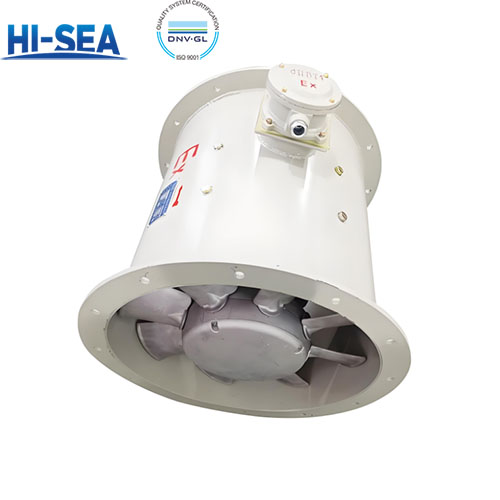
Marine Blower
Marine blowers are devices used to increase gas pressure and gas flow. It is driven primarily by mechanical and electrical power to generate airflow and increase the pressure of the gas. A blower generates gas pressure and gas flow through intake, compression and exhaust processes. It is widely used in many applications such as air conditioning systems, combustion equipment, exhaust systems, and so on. Blowers are used for transportation of gases. For example, clean air, clean gas, sulfur dioxide and other inert gases, etc. It can also be used to produce and transport other special gases such as flammable, explosive and corrosive gases as required.
Overview
Merits:
Small size and light weight: Marine fans are usually designed to be compact, so as to reduce the occupied space and weight and facilitate installation and transportation.
Low power: the power of marine fans is usually low to meet the requirements of marine power system.
Reversible: the reversible design of the fan enables it to rotate forward and backward when necessary, increasing the flexibility of use.
Smooth operation: the marine fan runs smoothly, reducing noise and vibration and providing a more comfortable experience.
Anti-shock and vibration: Because ships will encounter various complex environments during sailing, marine fans need to have good anti-shock and vibration capabilities to ensure long-term stable operation.
Good anti-corrosion performance: marine fans usually adopt anti-corrosion materials and designs to adapt to the corrosiveness of the marine environment.
Convenient disassembly: the structural design of the fan takes into account the convenience of disassembly, such as the openable casing of the axial flow fan, which is convenient for maintenance and replacement on the ship.
Explosion-proof design: Marine explosion-proof fan is specially designed to reduce the concentration and temperature of dangerous gas within the explosion limit, provide good ventilation conditions and ensure safety.
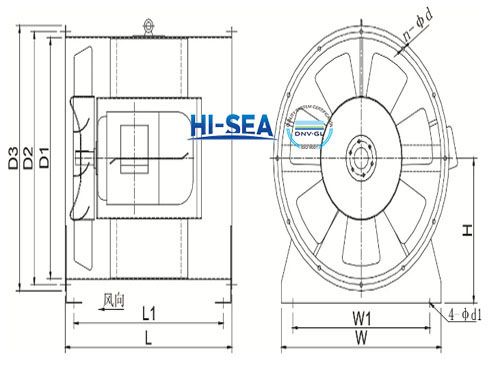
Drawing:
Picture:






